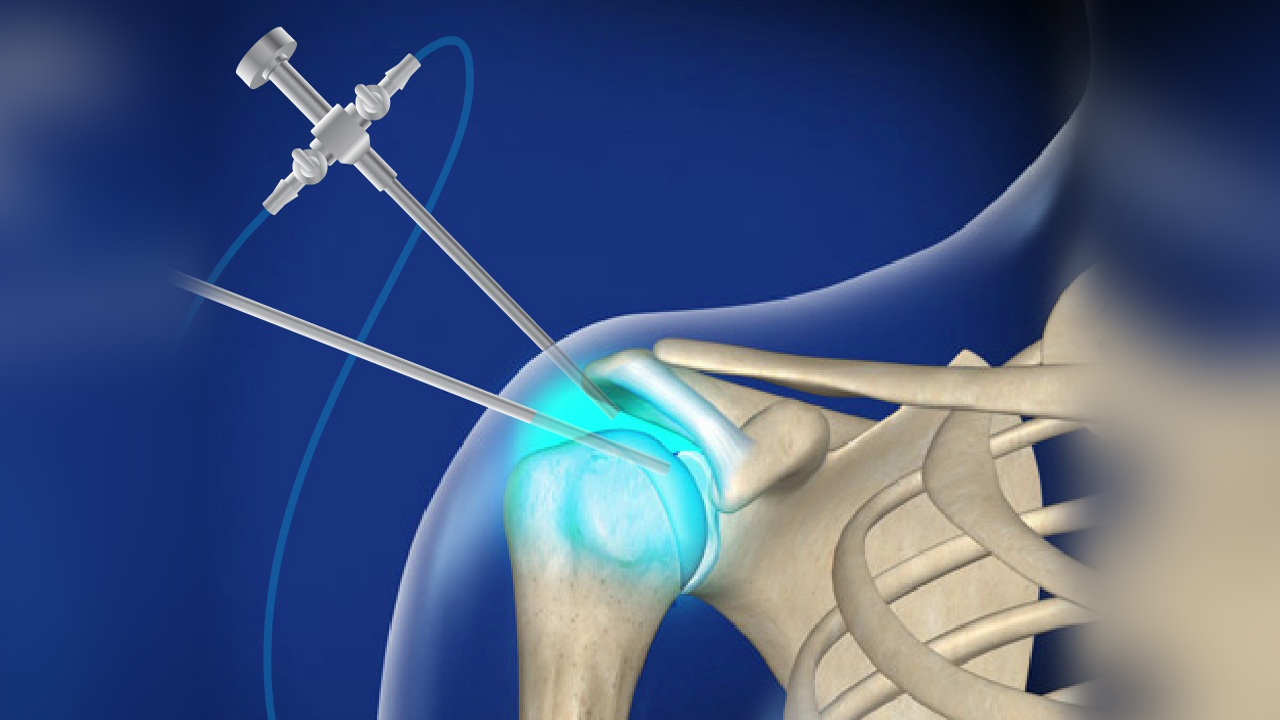
What is Diagnostic-shoulder ?
"Diagnostic shoulder" is not a specific medical term but rather a phrase that may be used to refer to various diagnostic procedures, tests, or examinations performed to assess and diagnose shoulder-related conditions, injuries, or disorders. These diagnostic methods are employed by healthcare professionals to identify the cause of shoulder pain, discomfort, or dysfunction and to develop an appropriate treatment plan. Here are some common diagnostic methods used for shoulder issues:
-
Physical Examination: Healthcare providers often begin with a physical examination to evaluate the range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder. They may ask about symptoms and medical history to help with the diagnosis.
-
Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: X-rays can provide images of the bones in the shoulder and can help identify fractures, arthritis, and some structural issues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans offer detailed images of the soft tissues in the shoulder, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. This is particularly useful for diagnosing rotator cuff tears, labral tears, and other soft tissue injuries.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound is often used to examine the shoulder's tendons, muscles, and other soft tissues in real-time. It can help assess for issues like tendonitis, bursitis, or fluid accumulation.
-
CT Scan:
In some cases, a computed tomography (CT) scan may be performed to provide detailed cross-sectional images of the shoulder, which can be especially helpful for evaluating complex fractures or bone-related issues.
-
Arthroscopy:
This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) into the shoulder joint through a small incision. It allows direct visualization of the inside of the shoulder joint and can be both diagnostic and therapeutic.
-
Blood Tests:
Blood tests may be ordered to rule out systemic conditions that could be contributing to shoulder symptoms, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG):
If nerve-related issues are suspected, NCS and EMG may be used to assess the function of nerves and muscles in the shoulder and upper arm.
The choice of diagnostic method depends on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and the suspected underlying condition. Once a diagnosis is established, healthcare providers can develop a treatment plan tailored to the specific issue, which may include physical therapy, medication, rest, exercises, or surgical intervention, as needed. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on managing shoulder problems.