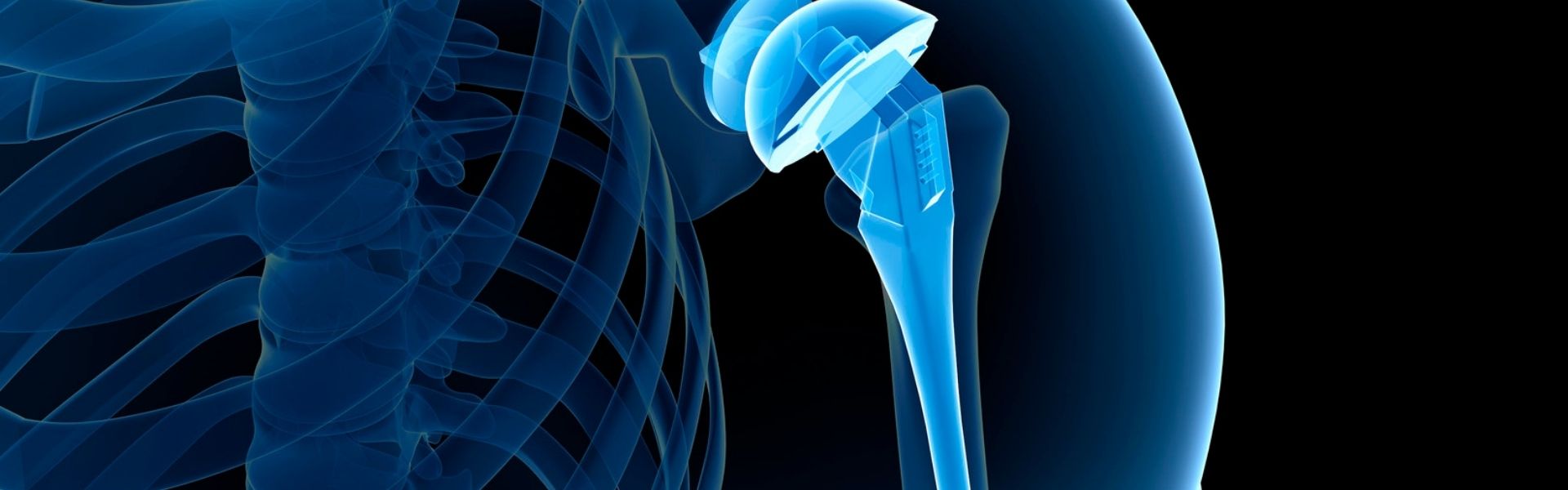
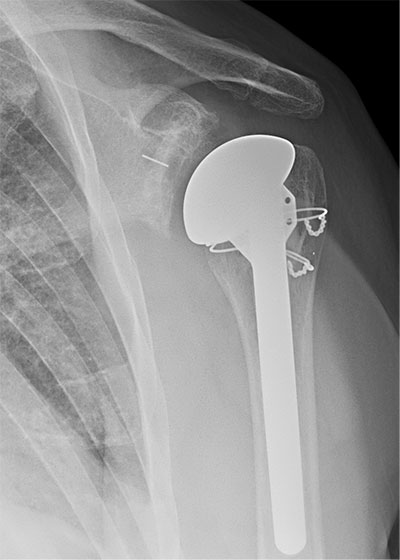
What is Anatomical Shoulder Replacement ?
An anatomical shoulder replacement, also known as total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA), is a surgical procedure performed to treat severe shoulder joint pain and dysfunction, typically caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or severe fractures of the shoulder joint. This procedure involves replacing the damaged or worn-out parts of the shoulder joint with artificial components to restore function and alleviate pain.
Here's an overview of how an anatomical shoulder replacement is performed:
-
Patient Evaluation: Before surgery, a thorough evaluation is conducted to assess the patient's overall health, shoulder condition, and any other medical issues that may affect the surgery or recovery.
-
Anesthesia:
The patient is placed under general anesthesia, which means they are asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
-
Incision:
The surgeon makes an incision on the front of the shoulder, typically several inches long, to access the shoulder joint.
-
Joint Exposure:
The surgeon carefully moves aside the surrounding muscles and tissues to access the shoulder joint.
-
Bone Preparation:
The damaged or arthritic portions of the shoulder joint (the humeral head and glenoid) are removed. The surgeon reshapes the bones to prepare them for the artificial components.
-
Implant Placement:
The artificial components, which typically consist of a metal stem and a plastic or metal socket, are then inserted into the prepared bone. The humeral component is inserted into the upper arm bone (humerus), and the glenoid component is placed into the shoulder socket (glenoid).
-
Closure:
Once the components are securely in place, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples.
-
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
After the surgery, the patient is monitored in the recovery area and then moved to a rehabilitation program. Physical therapy and exercises are an essential part of the recovery process to help regain shoulder strength and range of motion.
An anatomical shoulder replacement is designed to mimic the natural anatomy of the shoulder joint as closely as possible, allowing for improved function and reduced pain. It is an effective treatment option for patients with advanced shoulder joint problems who have not responded to non-surgical treatments.
It's important to note that the success of a shoulder replacement surgery depends on various factors, including the patient's overall health, compliance with post-operative rehabilitation, and the skill of the surgeon. Like all surgical procedures, there are risks and potential complications associated with anatomical shoulder replacement, and patients should discuss these with their healthcare providers before undergoing the surgery.