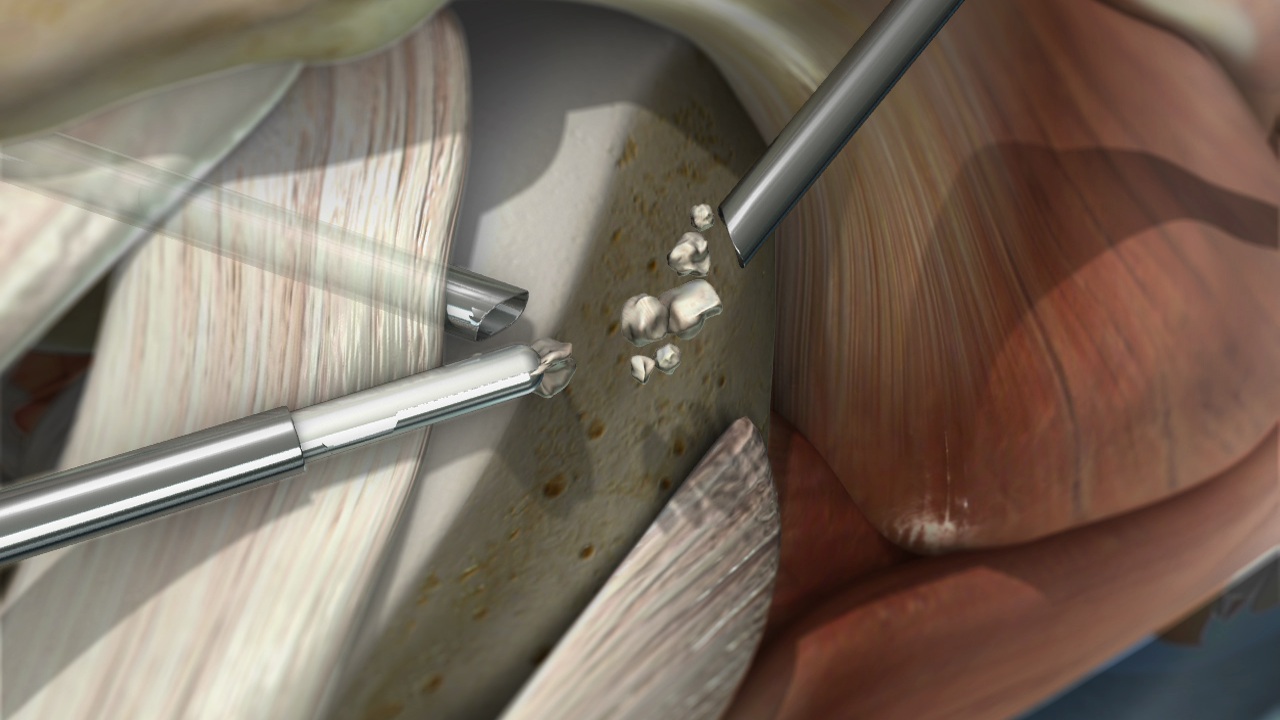
What is Loose Body Removal treatment ?
A loose body, in a medical context, refers to a small fragment or foreign object that becomes detached from its normal location within a joint, body cavity, or other anatomical structure. Loose bodies can vary in size and composition, and they can cause a range of symptoms and health issues depending on their location and nature.
Here are some common types of loose bodies in different parts of the body:
-
Joint Loose Bodies: Loose bodies within a joint are often composed of cartilage, bone, or soft tissue. These can result from various conditions, including joint injuries, osteoarthritis, or certain types of arthritis. They can cause pain, swelling, catching or locking sensations, and reduced joint mobility.
-
Intra-abdominal Loose Bodies:
Intra-abdominal loose bodies can include small masses, cysts, or foreign bodies that become detached within the abdominal or pelvic cavities. These may cause pain, discomfort, or bowel obstruction if they block the normal flow of fluids or organs.
-
Intra-articular Loose Bodies:
Loose bodies can also form within synovial joints (the joints containing synovial fluid). These bodies can be made of bone or cartilage and can impair joint function, causing pain and inflammation.
Treatment for loose bodies depends on their location, size, and impact on the individual's health.
Common approaches include:
-
Surgical Removal: Many loose bodies require surgical removal, especially if they are causing pain, impeding joint function, or posing a risk to other organs or structures. Surgery can often be performed arthroscopically (for joint loose bodies) or using other minimally invasive techniques.
-
Medication:
In some cases, medications may be used to dissolve or shrink loose bodies composed of certain materials, such as urate crystals in the case of gout.
-
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy may be recommended after the removal of joint loose bodies to help restore range of motion and strength to the affected joint.
-
Management of Underlying Conditions:
In cases where loose bodies result from underlying conditions like arthritis, managing the underlying condition may help prevent the formation of new loose bodies.
It's important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a loose body or are experiencing symptoms related to one. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation, including imaging studies like X-rays or MRI, to diagnose the presence and location of a loose body and recommend appropriate treatment. Left untreated, loose bodies can cause ongoing pain, joint damage, and other complications.