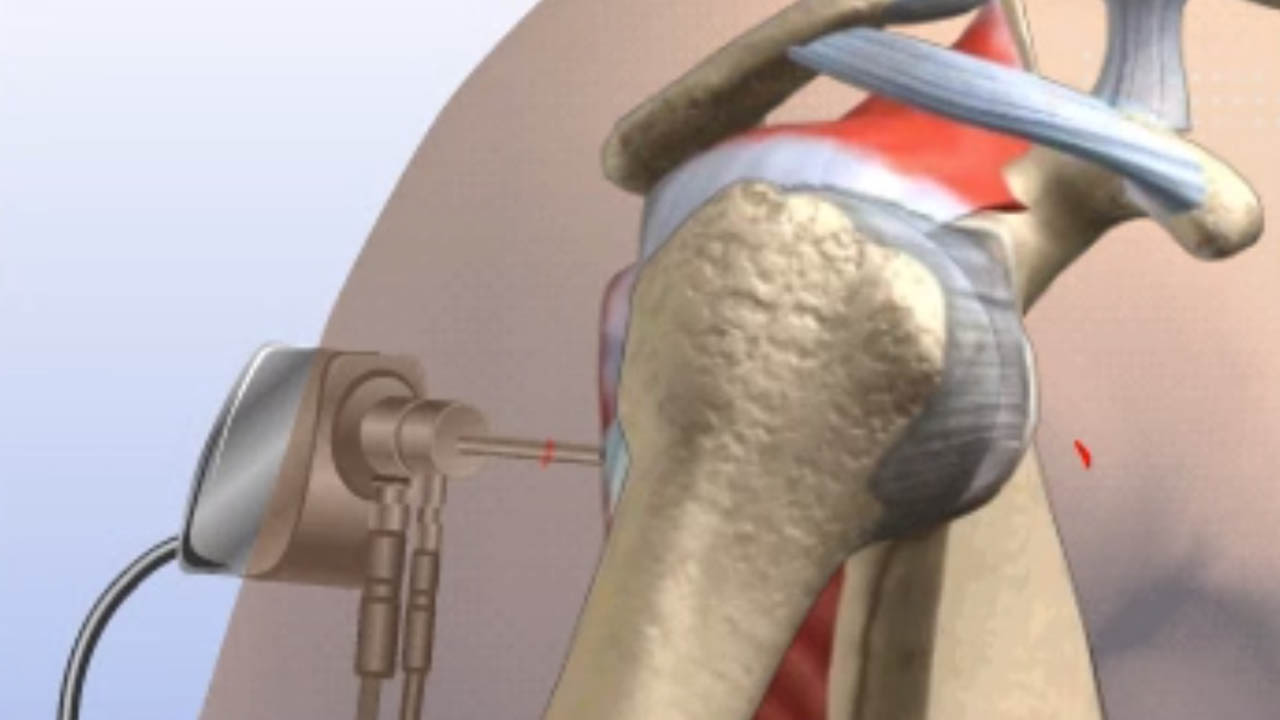
WHAT IS TRIMMINGOF-TORN-LABRUM ?
Trimming of a torn labrum is a surgical procedure performed to address a tear or damage to the labrum in the shoulder or hip joint. The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the joint, providing stability and cushioning. Labral tears can cause pain, instability, and limited range of motion in the affected joint. Trimming is one of the surgical techniques used to treat these tears, and it involves the removal of the damaged or torn portion of the labrum.
Here is an overview of the procedure:
-
Patient Evaluation: Before surgery, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, including physical examinations and imaging studies (such as MRI), to confirm the presence and extent of the labral tear and to assess overall joint health.
-
Anesthesia:
The patient is placed under anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. The type of anesthesia used (local, regional, or general) may vary depending on the patient and the surgeon's preference.
-
Arthroscopy:
In most cases, trimming of a torn labrum is performed arthroscopically. This minimally invasive technique involves making small incisions around the joint and inserting an arthroscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera on one end, to provide a clear view of the joint's interior.
-
Tear Assessment:
The surgeon examines the labrum and identifies the torn or damaged portion. The extent and location of the tear determine the amount of tissue that needs to be trimmed or removed.
-
Trimming:
Using specialized surgical instruments, the surgeon trims away the torn or frayed edges of the labrum, removing any loose or damaged tissue. The goal is to create a stable and smooth labral edge that can function properly.
-
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
After the trimming procedure is completed, the surgeon closes the incisions, and the patient is typically allowed to go home on the same day. Recovery and rehabilitation are essential components of the recovery process. Physical therapy and exercises are often prescribed to help regain strength, range of motion, and joint stability.
It's important to note that not all labral tears require trimming, and the specific treatment approach may vary based on factors like the size and location of the tear, the patient's age, and their activity level. In some cases, labral tears can be repaired rather than trimmed. Repair involves stitching the torn labrum back together, which is generally preferred for younger individuals and those with larger, more significant tears.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with trimming of a torn labrum, and patients should discuss these with their healthcare provider and orthopedic surgeon. The success of the procedure and the recovery process depend on factors like the extent of the damage, the patient's adherence to post-operative instructions, and the effectiveness of rehabilitation efforts.